Brain Tumor
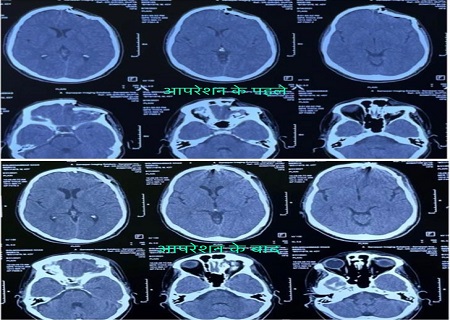
Treatment for a brain tumor can vary significantly depending on the type, location, size, and grade of the tumor, as well as the overall health and preferences of the patient
Treatment for a brain tumor can vary significantly depending on the type, location, size, and grade of the tumor, as well as the overall health and preferences of the patient. Here's a general overview of the main treatment options for brain tumors:
Surgery: Surgery is often the first-line treatment for brain tumors when it is safe and feasible to remove the tumor. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible without causing damage to critical brain structures. Neurosurgeons use advanced techniques such as image-guided surgery and intraoperative MRI to enhance precision. In some cases, complete removal may not be possible due to the tumor's location.
Radiation Therapy:
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): High-energy X-rays are targeted at the tumor from outside the body. EBRT is often used after surgery to eliminate remaining cancer cells or as the primary treatment when surgery is not an option.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS): This is a non-invasive technique that delivers highly focused radiation beams precisely to the tumor. It's often used for small tumors or when surgery is not possible.
Proton Therapy: Proton therapy is a specialized form of radiation therapy that can target tumors with even greater precision, minimizing damage to healthy surrounding tissues.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill or slow the growth of cancer cells. It is often used in combination with surgery and/or radiation therapy, particularly for tumors that are difficult to reach with surgery or are highly aggressive.
Targeted Therapy: Some brain tumors have specific genetic or molecular abnormalities that can be targeted with medications designed to inhibit their growth. These targeted therapies are often used when standard chemotherapy is not effective.
Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy is a rapidly evolving field that aims to boost the body's immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. It is still under investigation for brain tumors, but some promising clinical trials are exploring its potential.
Corticosteroids: These drugs may be prescribed to reduce swelling and relieve symptoms caused by the tumor's pressure on the brain.
Supportive Care: Managing symptoms and side effects is an essential part of brain tumor treatment. This may include pain management, anti-nausea medications, physical therapy, and psychological support.
Clinical Trials: Patients with brain tumors may be eligible to participate in clinical trials, which offer access to experimental treatments that are not yet widely available. These trials can be an important option for some individuals.
It's important to note that the choice of treatment is highly individualized and depends on various factors, including the tumor type and stage, the patient's age and overall health, and the expertise of the medical team. Treatment plans are typically developed through a collaborative effort involving neurosurgeons, radiation oncologists, medical oncologists, and other specialists. Additionally, ongoing monitoring and follow-up care are crucial to assess the tumor's response to treatment and manage any potential side effects or recurrence.
What Our Patients Say
Aliquam a augue suscipit, luctus neque purus ipsum neque dolor primis libero at tempus, blandit posuere ligula varius congue cursus porta feugiat


“Dr.Gourav jatav sir is really good doctor by profession , knowledge and experience. He is very friendly and polite. Always give best opinion and treatment without caring about money.”


“Dr.Gourav jatav sir is really good doctor by profession , knowledge and experience. He is very friendly and polite. Always give best opinion and treatment without caring about money.”


“Got best suggestions got relief spine problem without surgery within a 15 days of time I was suffering from last 3 years
Thanku doctor”


“Very polite, humble, listen to complains patiently and best is he advise surgery only when required.
Less tablets to eat.”


“Dr.gorav sir is the best me abhari hu aapka jo aapne mujhe nai jindgi di aap ka ahshan kabhi nahi bhul sakta har mahine aapse milne aana mera kartvya he aapke per chhune jarur aaunga sir bahut bahut dhanyawad aapka dil se sir”


“Best Surgeon , Thank you very much Dr. Gourav. Papa is is almost fine . On only 8% expectation you did it to save him. We are very thankful of you. May god always bless you Dr. And you are also not less than a god.”