Traumatic Spine Injury
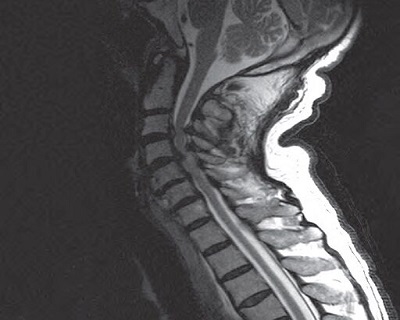
Traumatic spine injury refers to damage or injury to the spinal cord or the surrounding structures of the spine due to a traumatic event. These injuries can have serious and potentially life-changing consequences, affecting a person's mobility, sensation, and even their ability to perform daily activities. Traumatic spine injuries can result from various accidents and incidents, such as falls, car accidents, sports injuries, or acts of violence.
Traumatic spine injury refers to damage or injury to the spinal cord or the surrounding structures of the spine due to a traumatic event. These injuries can have serious and potentially life-changing consequences, affecting a person's mobility, sensation, and even their ability to perform daily activities. Traumatic spine injuries can result from various accidents and incidents, such as falls, car accidents, sports injuries, or acts of violence. Here are some key points to consider regarding traumatic spine injuries:
Types of Traumatic Spine Injuries:
Spinal Cord Injury (SCI): This type of injury involves damage to the spinal cord itself, leading to partial or complete loss of function below the level of the injury.
Vertebral Fractures: Fractures of the vertebrae can occur, potentially causing instability and damage to the spinal cord or nerves.
Soft Tissue Injuries: Trauma to the soft tissues around the spine, including muscles, ligaments, and discs, can also occur.
Symptoms and Severity: The severity of traumatic spine injuries varies widely depending on the location and extent of the damage. Common symptoms can include pain, loss of sensation, muscle weakness or paralysis, difficulty breathing (in the case of high cervical injuries), and loss of bowel or bladder control.
Emergency Care: Immediate medical attention is crucial for individuals with traumatic spine injuries. Emergency responders will often immobilize the spine to prevent further damage during transportation to the hospital. This may involve using a rigid cervical collar and a backboard.
Diagnostic Imaging: Diagnostic tests such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans are used to assess the extent and location of the spinal injury. These imaging studies help guide treatment decisions.
Treatment Options:
Conservative Treatment: Some spinal injuries may be managed non-surgically with immobilization (e.g., bracing or traction), medication for pain and inflammation, and physical therapy.
Surgery: Surgery may be required to stabilize the spine, remove bone fragments or foreign objects, and decompress the spinal cord or nerves. The type of surgery depends on the specific injury.
Rehabilitation: After the initial treatment, rehabilitation is essential for regaining function. This may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and vocational counseling.
Supportive Care: Patients with spinal cord injuries may require long-term care to manage complications such as pressure sores, urinary tract infections, and respiratory problems.
Prognosis: The outcome of traumatic spine injuries varies widely depending on the severity and location of the injury. Some individuals may regain partial function through rehabilitation, while others may have permanent disabilities.
Prevention: Many traumatic spine injuries are preventable through safety measures such as using seat belts, wearing helmets during sports and recreational activities, practicing fall prevention in older adults, and taking precautions to prevent violence and accidents.
It's essential for individuals who have experienced a traumatic spine injury to receive prompt and comprehensive medical care from a team of healthcare professionals, including trauma surgeons, neurosurgeons, and rehabilitation specialists. The goal of treatment is to maximize recovery and improve the individual's quality of life to the greatest extent possible.
What Our Patients Say
Aliquam a augue suscipit, luctus neque purus ipsum neque dolor primis libero at tempus, blandit posuere ligula varius congue cursus porta feugiat


“Dr.Gourav jatav sir is really good doctor by profession , knowledge and experience. He is very friendly and polite. Always give best opinion and treatment without caring about money.”


“Dr.Gourav jatav sir is really good doctor by profession , knowledge and experience. He is very friendly and polite. Always give best opinion and treatment without caring about money.”


“Got best suggestions got relief spine problem without surgery within a 15 days of time I was suffering from last 3 years
Thanku doctor”


“Very polite, humble, listen to complains patiently and best is he advise surgery only when required.
Less tablets to eat.”


“Dr.gorav sir is the best me abhari hu aapka jo aapne mujhe nai jindgi di aap ka ahshan kabhi nahi bhul sakta har mahine aapse milne aana mera kartvya he aapke per chhune jarur aaunga sir bahut bahut dhanyawad aapka dil se sir”


“Best Surgeon , Thank you very much Dr. Gourav. Papa is is almost fine . On only 8% expectation you did it to save him. We are very thankful of you. May god always bless you Dr. And you are also not less than a god.”